- The main industrial printing processes that DNS company are involved :
- Offset lithography.
- Flexography.
- Digital printing: inkjet & xerography.
- Gravure.
- Screen printing.
- security printing
Product Description
Starting An Offset Printing Press
A properly run offset printing press can be your passport to wealth. But if you do not know what you are doing, it’s a fast way to lose money. An offset printing press’ output is far more than that of digital, tarpaulin or screen printers. Presently, it is the only cost effective printing process that can produce thousands or millions of copies.

There are two main types of offset press. The most common is the sheet-fed type, so called because the paper stock it uses is in the form of cut sheets. For the largest jobs, companies usually use the web press; here the paper stock comes in the form of huge rolls of paper. Some of the products an offset press can produce are packaging, posters, forms, books and newspapers.
Putting up a printing press is capital intensive; you will need at least P1 million to start. This will enable you to buy a small second-hand press and paper cutter. Set aside capital for supplies and other working capital needs as well. However, this is just the smallest set-up and there are many jobs you cannot handle. Fortunately, you can rent other printers’ equipment if your machine is not capable.
Looking For A Suitable Location
•Make sure the area is properly zoned for a printing press. A printing press is considered as a manufacturing facility and may not be allowed in many locations.
•Make sure there is a three-phase electrical supply. Printing press equipment usually need this. Although you can use a converter, this tends to be more costly and may damage your machine.
•Check if a location has termites or is prone to flooding. Since paper is the main material used, care must be taken to protect against damage.
•The ceiling should be high for better air circulation. The big machines generate a lot of heat and if you cannot afford air conditioning the press floor, then at least have sufficient air flowing.
•Make sure there is sufficient floor area. Besides the area for the printing press and other equipment, there must be a space for the bindery, prepress, supply room, finished products room and office.
Getting The Right Equipment
•Choose the machine that can best produce your primary products.
•Avoid buying used equipment. If your budget permits, it is best if you get brand new equipment not only to avoid breakdowns but also to offer better quality.
•It is usually better to buy a two-color or four-color machine rather than a single color press. Although a one-color machine can produce all the colors of a four-color machine, the two-color or four-color press’ output is many times faster.
•Be careful in buying cheap brands. They may not be capable of giving quality output. Another potential problem is the availability of spare parts.
Costing And Pricing
It is strongly suggested that you know how to cost and price your printing service so that you can find out how much you should be earning. Being the one to cost also forces you to know about the printing process. This knowledge will enable you to save on costs.
Starting a printing press needs careful study since you will be investing a substantial amount of capital. It is highly suggested that you attend a seminar on the topic before proceeding.
Flexo
In flexography the content that needs to be printed is on a relief of a printing plate, which is made from rubber. This plate is inked and that inked image is subsequently transferred to the printing surface. The process can be used to print on paper as well as plastics, metals, cellophane and other materials. Flexo is mainly used for packaging and labels and to a lesser extent also for newspapers.
 Some packaging printing is moving from flexo to digital.
Some packaging printing is moving from flexo to digital.
Digital printing
Digital printing can be done in various ways. Two technologies dominate the industry:
- Inkjet – In an inkjet printer the image that needs to be printed is created by small droplets of ink that are propelled from the nozzles of one or more print heads. Inkjet devices can print on a wide range of substrates such as paper, plastic, canvas or even doors and floor tiles. Inkjet printing is used a lot for posters and signage. It is also economical for short run publications such as photo books or small runs of books. In-line inkjet printers are sometimes combined with other types of presses to print variable data, such as the mailing addresses on direct mail pieces. The press shown below is the HP PageWide C500, meant for printing on corrugated board.

- Xerography – In xerographic printers, such as laser printers, the image that needs to be printed is formed by selectively applying a charge to a metal cylinder called a drum. The electrical charge is used to attract toner particles. These particles are transferred to the media that is being printed on. To make sure the toner is fixed properly, the substrate passes through a fuser that melts the toner into the medium. Laser printers are not only used in offices but also for small run printing of books, brochures and other types of document. These printers are also used for transactional printing (bills, bank documents, etc) and direct mail.
In 2009 both techniques jointly accounted for around 15% of the total volume of print.
 Digital printing is increasingly utilized for print jobs that were previously printing using offset, flexo or screen printing.
Digital printing is increasingly utilized for print jobs that were previously printing using offset, flexo or screen printing.
- In short run small format (A3 size) printing, digital is taking over from offset for both color and B&W printing. Quick printers and copy shops print digitally on presses from vendors like Xerox, HP, Canon, and Konica Minolta.
- Labels are also increasingly being printed digitally.
- Billboard and point-of-sale or point-of-purchase jobs are being done by wide-format inkjet devices.
- There is a wide range of small format printers used to print on phone cases, mugs and other products.
- In book printing publishing companies start to rely more on print-on-demand. The Espresso Book Machine pictured below is well suited for that job.

There are a number of other digital printing processes that are geared towards specific niche markets:
- Dye-sublimation is a printing process in which heat is used to transfer a dye onto the substrate. Dye-sub printers are mainly used for printing on textiles, for proofing and for producing photographic prints. Some printers can print on a variety of materials such as paper, plastic, and fabric.
- In the direct thermal printing process heat is used to change the color of a special coating that has been applied to paper. This process is used in cash registers but also to add markings, such as serial numbers, to products. For this a transparent ink is used that changes color when a laser applies heat to it.
- In the thermal ink transfer printing process heat is used to melt print off a ribbon and onto the substrate. It is used in some proofing devices but seems to be gradually disappearing off the market.
Gravure
Also known as rotogravure, this is a technique in which an image is engraved into a printing cylinder. That cylinder is inked and this ink subsequently transfers to the paper. Gravure is used for high volume work such as newspapers, magazines, and packaging.
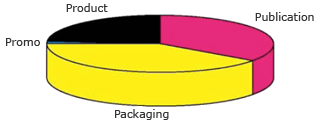 Gravure is gradually losing market share to offset for publication printing and to flexo for packaging applications.
Gravure is gradually losing market share to offset for publication printing and to flexo for packaging applications.
Screen printing
As its name implies, this printing technique relies on a screen, which is a woven piece of fabric. Certain areas of this mesh are coated with a non-permeable material. In the remaining open spaces ink can be pushed through the mesh onto a substrate. The advantage of screen printing is that the surface of the recipient does not have to be flat and that the ink can adhere to a wide range of materials, such as paper, textiles, glass, ceramics, wood, and metal.
The image below shows a screen printing press that is used to print t-shirts.
 Increasingly screen printing is being replaced by digital printing.
Increasingly screen printing is being replaced by digital printing.
Additional printing processes
- Letterpress – Once a dominant printing technique, letterpress is now used for business cards, wedding invitations,…
- Flocking – used to add a (colored) velvet-like texture to paper, textiles, etc.
- Pad printing – used to print on 3-dimensional surfaces.
- Intaglio – nowadays mainly used for used stamps and paper currency.
- Thermography – This is more of a finishing process than an actual printing process. It produces raised lettering on the printed side of the paper and is used for wedding invitations, letterheads, business cards,…
DNS-IRAN company, a leading business partner provider, conducts application on Starting any kind of Printing Press. Contact info@dns-iran.com or visit www.dns-iran.com for details.


